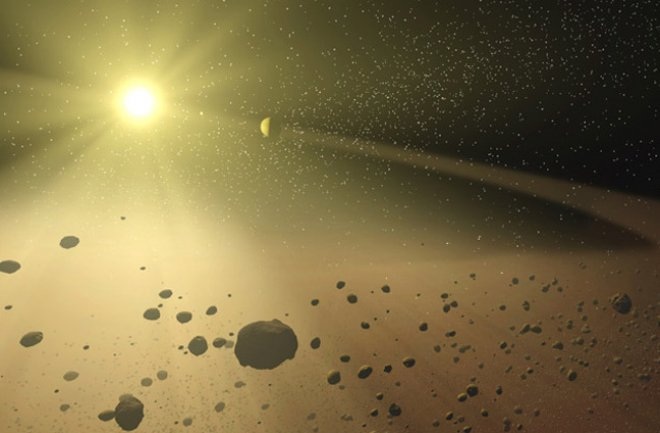
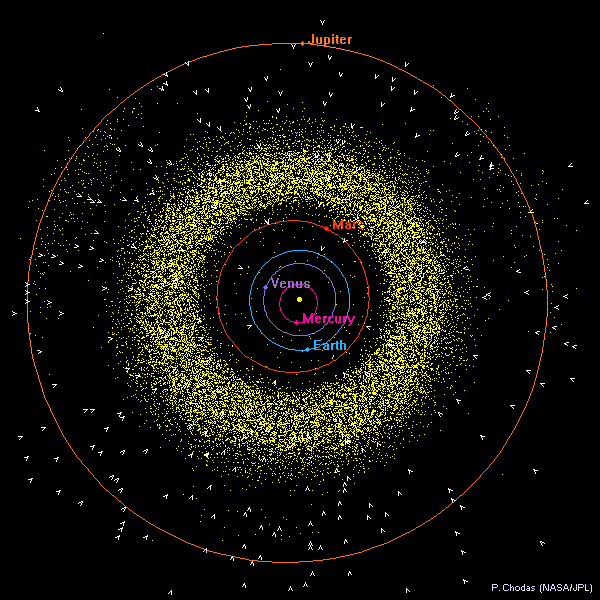
Inner Solar System Orbit DiagramsThese inner solar system diagrams show the positions of all numbered asteroids and all numbered comets on 2013 July 1. The orbits and positions of the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and Jupiter are also shown. Asteroids
are yellow dots and comets are symbolized by sunward-pointing wedges. The top diagram shows the view from above the ecliptic plane (the plane containing the Earth's orbit). The bottom diagram shows the view from the edge of the ecliptic plane. In both diagrams, the vernal equinox is to the right along the horizontal axis (+X direction). Only comets and asteroids in JPL's small-body database as of 2013 July 1 were used. |
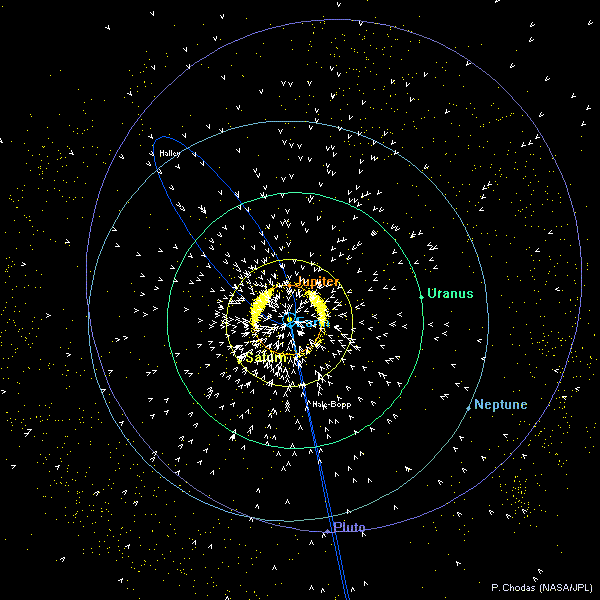
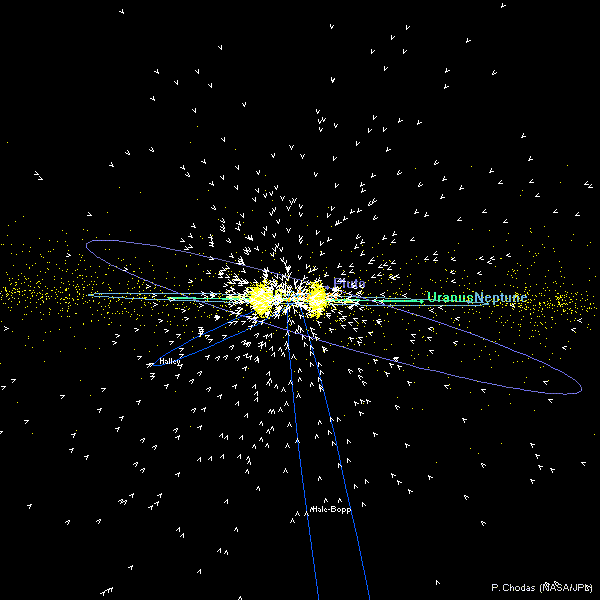
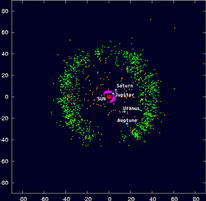
Outer Solar System Orbit DiagramsThese outer solar system diagrams show the positions of asteroids and comets with semi-major axes (a) greater than 5 AU (orbital periods greater than ~11 years) on 2013 July 1. The orbits and positions of Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto, and comets Halley and Hale-Bopp
are also shown. Asteroids are yellow dots and comets are symbolized by sunward-pointing wedges. The top diagram shows the view from above the ecliptic plane. The bottom diagram shows the view from the edge of the ecliptic plane. In both diagrams, the vernal equinox is to the right along the horizontal axis (+X direction). Only comets and asteroids in JPL's small-body database as of 2013 July 1 were used. |

The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. It is occupied by numerous irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids or minor planets. The asteroid belt is also termed the main asteroid belt or main belt to distinguish its members from other asteroids in the Solar System such as near-Earth asteroids and trojan asteroids.
Kuiper beltKuiper belt /ˈkjuːɪpər/ or /ˈkaɪpər/, sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt (after the astronomers Kenneth Edgeworth and Gerard Kuiper), is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets, extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive
|
http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?MCode=Dawnhttp://news.discovery.com/space/asteroids-meteors-meteorites/top-10-asteroid-deflection-130130.htm

4 Biggest Asteroid Strikes Ever
The devastating meteor crash in Russia made us wonder, how many other big strikes has the planet taken? Trace found out and counts down the top four biggest asteroid strikes to ever hit Earth! Huge Asteroid almost hits earthNASA's Asteroid Sample Return Mission Moves into Development
NASA's Asteroid Initiative Benefits From Rich History
|
the universe season 2
|