Light Warping/Mass Transfer Interactions Red/White Dwarf Binarys 05/04/13
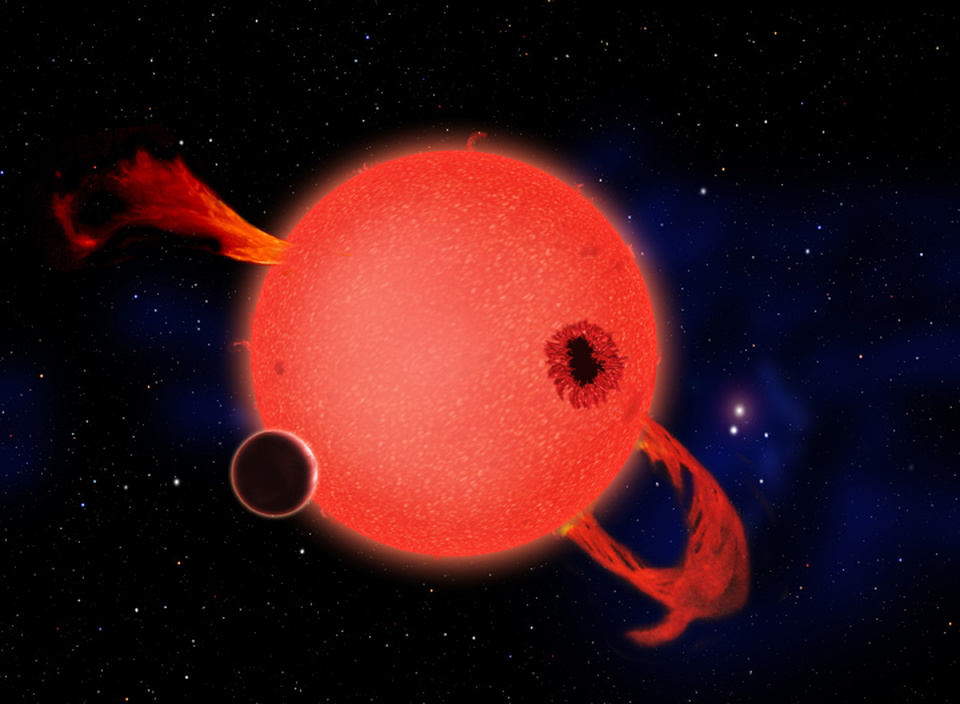
The dead star, also called a white dwarf, is the burnt-out core of what used to be a star like our sun. It is locked in an orbiting dance with its partner, a small "red dwarf" star. While the tiny white dwarf is physically smaller than the red dwarf, it is more massive. When the white dwarf passed in front of its star, its gravity caused the starlight to observably bend and brighten.
The dead star, also called a white dwarf, is the burnt-out core of what used to be a star like our sun. It is locked in an orbiting dance with its partner, a small "red dwarf" star. While the tiny white dwarf is physically smaller than the red dwarf, it is more massive. When the white dwarf passed in front of its star, its gravity caused the starlight to observably bend and brighten.

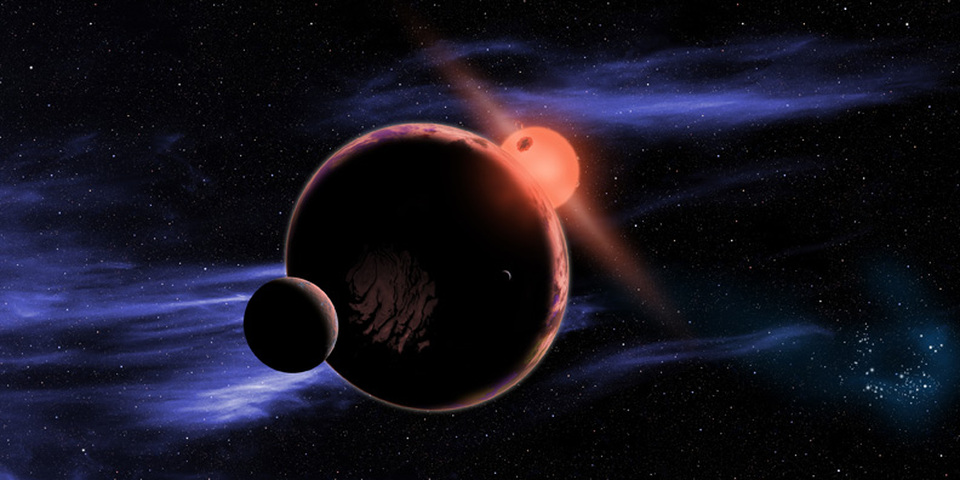
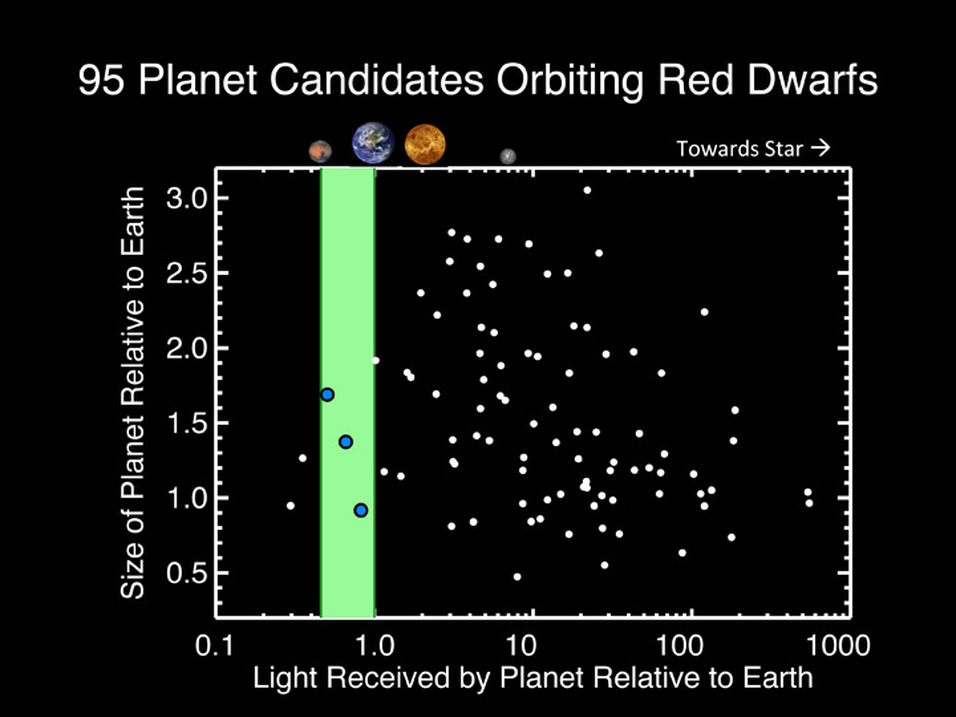
13.5 Billion Exo-earths Orbiting Red Dwarfs Across the Galaxy 14/03/13
Red Dwarf Stars May Be Best Chance for Habitable Alien Planets 23/02/12


Red Dwarfs Luminosity Between 1/10,000 and 10% of Sun 30/09/08


Red Dwarfs Compromise 70% of stars in Milky Way With Habitable Life Zones 11/01/08
The researchers were looking for habitable zones around red dwarf stars, which can be 50-90% smaller than the Sun and much cooler. The comprise 70% of the stars in the Milky Way, but they’re harder to spot because they put out less light.
They were surprised to learn that these red dwarf stars have tiny habitable zones. When they added up the habitable zones of 44 red dwarf stars nearby the Sun, they found they didn’t add up to equal the habitable zone of a single Sun like star.
Read more: http://www.universetoday.com/12423/red-dwarfs-have-teeny-tiny-habitable-zones/#ixzz2gsdgVid8
The researchers were looking for habitable zones around red dwarf stars, which can be 50-90% smaller than the Sun and much cooler. The comprise 70% of the stars in the Milky Way, but they’re harder to spot because they put out less light.
They were surprised to learn that these red dwarf stars have tiny habitable zones. When they added up the habitable zones of 44 red dwarf stars nearby the Sun, they found they didn’t add up to equal the habitable zone of a single Sun like star.
Read more: http://www.universetoday.com/12423/red-dwarfs-have-teeny-tiny-habitable-zones/#ixzz2gsdgVid8

Red Dwarf Kids Astronomy
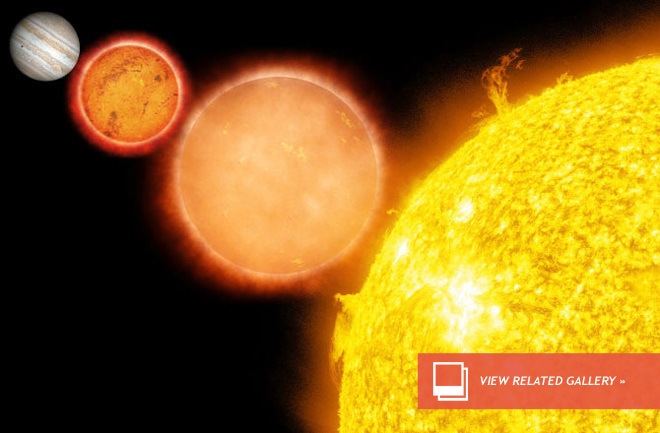
Red Dwarf stars are smaller than our sun. And since they are smaller, they also have less mass. Because of their small size, these stars burn their fuel very slowly, which allows them to live a very long time. This also causes these stars to not shine as brightly as others. Some red dwarf stars will live trillions of years before they run out of fuel.
Why are red dwarf stars red?
Because red dwarf stars only burn a little bit of fuel at a time, they are not very hot compared to other stars. Think of a fire. The coolest part of the fire is at the top of the flame where it glows red, the hotter part in the middle glows yellow, and the hottest part near the fuel glows blue. Stars work the same way. Their temperature determines what color they are. Thus, we can determine how hot a star is just by its color.
Red dwarf stars are by far the most common type of star in outer space. However, very few stars that you see in the sky are red dwarfs. This is because they are so small and make very little light. Imagine standing on a mountain. Pretend that there are one million kids 5 miles away holding flashlights, and 20 miles away there is a lighthouse for ships. You will most likely not see any of the flashlights, while you will very easily see the lighthouse. If the flashlights all glowed as brightly as the lighthouse they would blind you. Likewise, if all the red dwarf stars glowed as bright as the bigger stars, our nighttime sky would be very bright.
Red Dwarf stars are smaller than our sun. And since they are smaller, they also have less mass. Because of their small size, these stars burn their fuel very slowly, which allows them to live a very long time. This also causes these stars to not shine as brightly as others. Some red dwarf stars will live trillions of years before they run out of fuel.
Why are red dwarf stars red?
Because red dwarf stars only burn a little bit of fuel at a time, they are not very hot compared to other stars. Think of a fire. The coolest part of the fire is at the top of the flame where it glows red, the hotter part in the middle glows yellow, and the hottest part near the fuel glows blue. Stars work the same way. Their temperature determines what color they are. Thus, we can determine how hot a star is just by its color.
Red dwarf stars are by far the most common type of star in outer space. However, very few stars that you see in the sky are red dwarfs. This is because they are so small and make very little light. Imagine standing on a mountain. Pretend that there are one million kids 5 miles away holding flashlights, and 20 miles away there is a lighthouse for ships. You will most likely not see any of the flashlights, while you will very easily see the lighthouse. If the flashlights all glowed as brightly as the lighthouse they would blind you. Likewise, if all the red dwarf stars glowed as bright as the bigger stars, our nighttime sky would be very bright.